Think of project financial management as the art of planning, organising, and controlling every penny your project spends to make sure it hits its goals. It covers everything from the initial budgeting and cost estimation right through to constant monitoring and reporting. Done right, it turns a simple financial plan from a piece of paper into the project's lifeblood, making sure every pound is spent with purpose.
Understanding Your Project's Financial Backbone

Imagine your project's financial plan is its circulatory system. It’s not just about bean-counting; it's the engine that pumps resources like cash flow to every task, artist, and milestone. This perspective shifts finance from being a frustrating constraint to a powerful tool for success. It gives you the framework to make smart decisions, head off risks, and deliver the project on time and, crucially, within budget.
This process isn't a one-off task. It’s woven into the entire project lifecycle, changing its focus as you move through each stage:
- Planning Phase: This is where you lay the financial groundwork. You're deep in detailed cost estimations, setting a baseline budget, and making sure the funding is locked in.
- Executing Phase: Once the work starts, the focus shifts. Now you're tracking actual spending, managing procurement, and ensuring your resources are being used as efficiently as possible.
- Monitoring Phase: This is all about continuous oversight. You’re comparing what you've actually spent against the budget, forecasting what's to come, and analysing any differences to get things back on track.
For any project manager, a solid grip on this financial backbone is non-negotiable. Without it, even the most brilliantly creative project can crash and burn due to cash flow gaps, surprise cost overruns, and unhappy stakeholders. In fact, industry analysis consistently shows that projects with mature financial management practices are far more likely to hit their original targets.
The real job of project financial management is to make sure the project lands within its approved budget. It's about giving you the tools to spot financial trouble on the horizon before it becomes a full-blown crisis.
To give you a clear map, let’s break down the essential components you need to master. Think of these as the four pillars holding up any strong financial strategy, keeping everything clear from kickoff to final delivery.
The Four Pillars of Project Financial Management
These pillars provide the structure for sound financial decision-making throughout your project. Each one addresses a critical aspect of keeping the finances healthy and transparent.
| Pillar | Core Function | Key Activity Example |
|---|---|---|
| Budgeting and Cost Planning | Establishing a detailed financial baseline for all project activities. | Creating a work breakdown structure and assigning cost estimates to each task. |
| Forecasting and Analysis | Predicting future financial performance and identifying deviations from the plan. | Conducting monthly variance analysis to compare actual costs against the budget. |
| Cash Flow Management | Ensuring sufficient liquidity to cover project expenses as they arise. | Scheduling client invoicing and supplier payments to maintain a positive cash balance. |
| Governance and Reporting | Implementing controls and communicating financial health to stakeholders. | Establishing a change control board to approve any budget adjustments. |
By getting to grips with these pillars, you move beyond just tracking numbers. You become a strategic leader, capable of steering your project to financial stability and ultimate success. In the sections that follow, we'll dive deeper into each of these areas, giving you practical techniques and tools to use on your own projects.
Building a Realistic Project Budget and Cost Plan
Think of a project budget as more than just a spreadsheet of numbers. It’s the financial roadmap for your project, telling the story of how you'll get from A to B without running out of fuel. Getting this right from the start is absolutely essential for managing project finances effectively; it creates the baseline you'll measure everything against. Flying blind without one is a surefire way to get lost.
The whole process starts by translating your project's scope—every single deliverable, task, and milestone—into pounds and pence. A fuzzy scope always leads to a fuzzy budget, and that's just asking for cost overruns. The rule is simple: the more detailed your project plan, the sharper your financial plan will be.
Choosing Your Estimation Technique
How you land on your budget numbers is just as crucial as the numbers themselves. There are a few tried-and-tested techniques, and each one has its place. Let's pretend we're building a new company website to see how they stack up.
Top-Down Estimation: This is your quick-and-dirty, back-of-the-envelope calculation. You might look at similar website projects you've done before and say, "They usually come in around £50,000, so let's start there." It’s fast, but it’s a ballpark figure at best—really only useful for those initial "is this even feasible?" conversations.
Parametric Estimation: Here, we get a bit more scientific by using historical data. For instance, if you know from past experience that each webpage costs roughly £1,500 to design and develop, you can multiply that by the number of pages needed. So, 20 pages x £1,500 gives you a £30,000 estimate. It’s a step up in accuracy.
Bottom-Up Estimation: This is the most accurate method, but it’s also the most work. You break the entire project down into its smallest possible tasks—wireframing the homepage, writing copy for the 'About Us' page, front-end development, and so on. Then you cost out each tiny piece. Add them all up, and you get a highly detailed and defensible total budget.
A bottom-up approach is considered the gold standard for creating a defensible project budget. It forces you to think through every component, leaving less room for surprises and making it easier to justify costs to stakeholders.
Accounting for Every Type of Cost
A solid cost plan needs to put every expense in the right bucket. If you miss a category, it can throw your entire budget off track pretty quickly.
Your plan should always break costs down into:
- Direct Costs: These are the expenses you can point to and say, "That's for this project." It includes things like team salaries for your developers and designers, software licences, and any specific materials you need to buy.
- Indirect Costs: Often called overheads, these are the general costs of keeping the lights on that aren’t tied to a single project. Think office rent, utility bills, and admin salaries. A fair portion of these costs gets allocated to your project.
- Contingency Reserves: This is your safety net, and it's non-negotiable. It’s a specific pot of money set aside for the "known unknowns"—risks you've identified that might happen. Maybe a key developer gets sick, or a tricky software integration takes longer than planned. It's not a slush fund; it's a calculated buffer for specific risks.
Organising your budget this way is a massive help when it comes to tracking and control. Some industries, like construction, live and die by this level of detail and often rely on specialized construction accounting to manage the complex mix of direct and indirect costs.
Ultimately, building a realistic budget comes down to diligence. You need a crystal-clear scope, the right estimation technique for the job, and a thorough accounting of every potential cost. For those looking to go deeper, you can learn more about the whole process in our detailed guide to project budgeting and controlling. This foundational work ensures your project not only starts on solid financial ground but has what it takes to stay there.
Mastering Forecasting and Variance Analysis
Once a project goes live, that meticulously crafted budget you laboured over stops being a plan and becomes your yardstick. It’s the baseline you’ll measure every single financial decision against. This is precisely where forecasting and variance analysis step in, acting as your project’s financial early-warning system. They help you shift from putting out fires to making smart, strategic moves.
Think of it like this: your budget is the route you've plotted on a map for a long road trip. Forecasting is checking the live traffic up ahead to spot potential delays. Variance analysis is glancing in the rearview mirror to see if you’ve strayed off course. Together, they get you to your destination on time and without running out of fuel.
The Power of Looking Ahead
Good financial management of projects is all about seeing beyond what you’ve already spent. Forecasting uses your current performance data to predict where you’ll end up, answering that crucial question: "Based on how things are going, where will we land financially?" This forward-looking view is absolutely vital for making course corrections before it’s too late.
Regular forecasting helps you anticipate cash flow needs, shift resources to where they’re actually needed, and manage what your stakeholders expect with a lot more confidence. Without it, you’re basically driving blind, only realising you’re over budget when the damage has already been done.
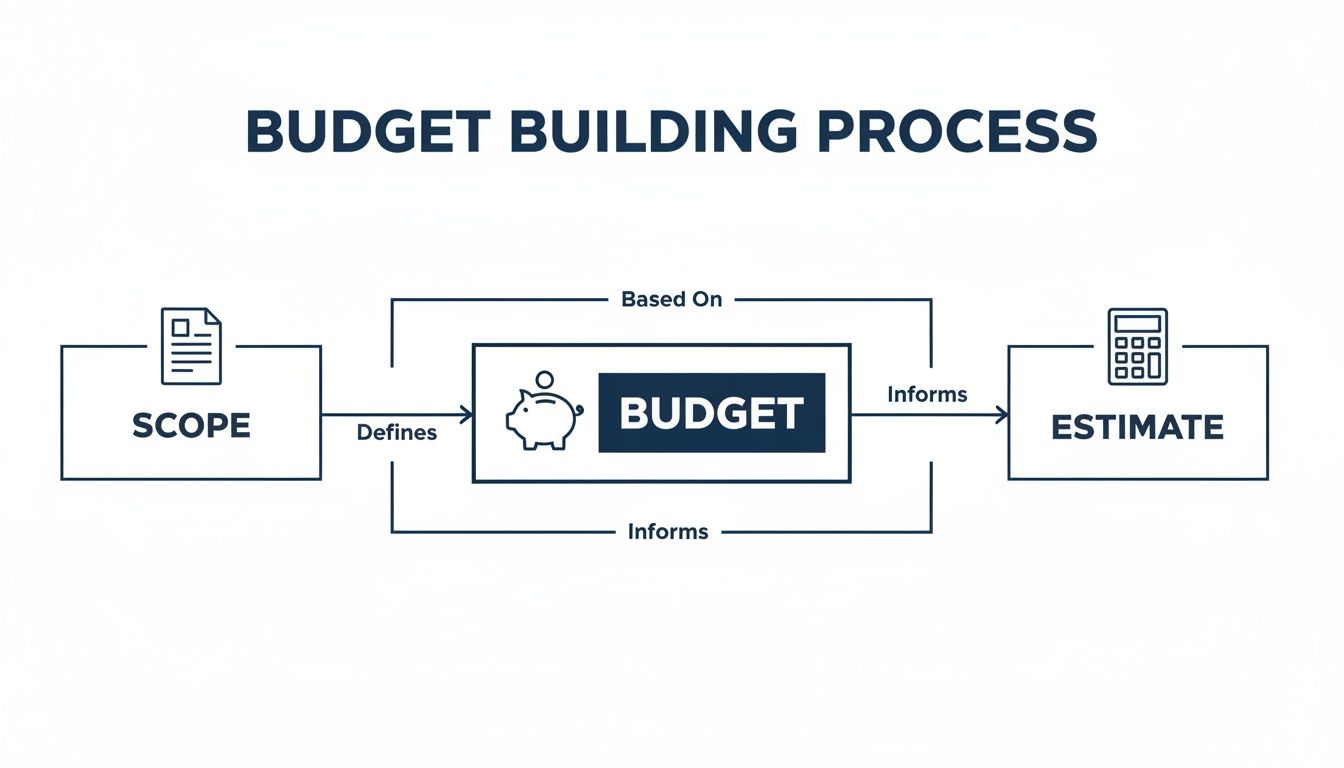
This simple flow shows that a solid budget is built on a clear scope and detailed estimates. Get that foundation right, and your forecasts will be much more accurate.
Unpacking Variance Analysis
Variance analysis is where you get down to brass tacks, comparing your planned budget against your actual costs. A variance is just the difference between what you thought you’d spend and what you actually spent. But this simple number tells a deep story about your project’s financial health and how efficiently your team is working.
Variance isn't just a number; it's a diagnostic tool. A negative variance might point to scope creep or an inefficient artist, while a positive one could mean you got a great deal on a licence or a task was finished way ahead of schedule.
To really get a handle on this, it helps to understand strategic budgeting and forecasting techniques. This knowledge helps you put the numbers into context, turning raw data into real, actionable intelligence.
The challenge of making budgets match reality is everywhere. For instance, recent UK public sector reports show massive differences between planned and actual spending. Sometimes capital projects can underspend by as much as 9.5%, while resource spending goes up because programme needs have changed. It’s a constant balancing act.
Earned Value Management: A Powerful Tool
One of the most solid ways to tie all this together is with Earned Value Management (EVM). It’s a method that integrates your scope, schedule, and cost data to give you a clear, objective snapshot of how your project is really doing. It all boils down to a few key metrics:
- Planned Value (PV): The budgeted cost of work you planned to have done by now.
- Actual Cost (AC): The real money you’ve spent to get that work done.
- Earned Value (EV): The value of the work you’ve actually completed, based on the original budget.
With these three figures, you can calculate crucial variances. For example, your Cost Variance (CV) is simply EV - AC. If it’s negative, you’re over budget. If it's positive, you’re under. Getting your head around the calculation of earned value is a game-changer for any project manager who's serious about financial control. It takes you way beyond a simple "budget vs. actuals" and gives you a true measure of performance.
Using KPIs and Governance for Strong Financial Control
Keeping your project's finances in check is about more than just having tidy spreadsheets. It demands a proper governance framework and the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to actually steer the ship. Think of governance as the rules of the road for your project's money, while KPIs are the dials on your dashboard telling you how you're doing. Without both, even the most carefully planned budget can go off the rails fast.
Building this framework starts with defining who has the authority to make financial decisions. When roles and responsibilities are crystal clear, you avoid confusion and ensure everyone knows who can sign off on expenses. This is the bedrock of accountability in the financial management of projects.
A key part of this is setting clear approval thresholds. For instance, a team lead might have the green light for expenses up to £500, but anything more needs a signature from the project manager. This kind of tiered system means senior eyes are on the big-ticket items, without creating bottlenecks for small, everyday spending.
Governance isn't about wrapping your project in red tape. It's about creating a predictable, transparent system for making financial decisions that builds trust with stakeholders and protects the bottom line.
Key Performance Indicators That Matter
While variance analysis is a must-do, it only tells you part of the story. To really get a handle on your project's financial health, you need to be tracking a wider set of KPIs. These metrics go beyond a simple "budget vs. actual" comparison to measure how efficiently you're working and the value you're creating.
Here are a couple of essential KPIs to get on your dashboard:
Cost Performance Index (CPI): This is the ultimate efficiency metric. It shows you exactly how much value you're getting for every pound you spend. A CPI over 1.0 means you're under budget for the work you've done, while anything less than 1.0 means you're over budget.
- Formula: CPI = Earned Value (EV) / Actual Cost (AC)
- Example: Let's say you've completed £50,000 worth of work (EV) but have spent £60,000 (AC) to get there. Your CPI is 0.83, signalling that you’re only getting 83 pence of value for every pound spent.
Return on Investment (ROI): This is the big one for measuring profitability. It compares the financial benefit of the project to what it cost. ROI is crucial for justifying the project's existence and showing its value to the business.
- Formula: ROI = (Net Profit / Project Cost) x 100
- Example: A project that cost £200,000 and generated a net profit of £50,000 has an ROI of 25%.
Metrics like these are the language stakeholders understand. They paint a clear, data-driven picture of how the project is performing, which leads to smarter decisions. For a deeper look into these concepts, feel free to explore our other resources on effective project financial control.
Managing Change with a Formal Process
No matter how well you plan, things change. That's why a solid change control process is so important for managing any tweaks to the budget. When a change request pops up that has financial implications, it needs to be formally reviewed, approved, and documented. This stops scope creep from quietly eating away at your project's finances.
A structured approach ensures that any adjustments to the budget are deliberate and properly accounted for. This is especially true on large-scale initiatives where tiny percentage swings can mean massive sums of money. Take UK Research and Innovation, for example. They manage a budget of around £9.78 billion. A variance of just 0.3% could represent an underspend of £22 million, showing just how critical careful planning is. You can see more on how large UK organisations tackle these financial realities in their latest annual report.
By blending a strong governance framework, insightful KPIs, and a formal change process, you create a powerful system for financial oversight. This structure doesn't just keep your project on track; it delivers the transparency and accountability you need to keep stakeholders confident from start to finish.
Choosing the Right Tools for Financial Tracking
Trying to manage project finances with manual spreadsheets is like trying to navigate a complex film shoot with a hand-drawn map. Sure, it might get you there eventually, but it’s slow, riddled with potential errors, and makes it incredibly difficult to pivot when things inevitably change. This is where modern, integrated tools come in, replacing outdated methods with precision and automation.
These platforms become the single source of truth for all your project's financial data. Forget about spending hours manually punching in timesheets or cross-referencing invoices. The right software handles these critical but tedious jobs for you, freeing you up to focus on making smart, strategic decisions instead of getting buried in data entry.
Moving Beyond Manual Spreadsheets
Making the leap from manual tracking to an automated system isn't just about convenience; it brings real, practical advantages that directly boost your bottom line and operational efficiency. The aim is to get a crystal-clear, live view of your project's financial health, without all the manual grunt work.
Here’s what you gain by bringing in an integrated tool:
- Greater Accuracy: Automation strips away the human error that’s always a risk with manual data entry. Your financial reports become something you can actually trust.
- Real-Time Visibility: Key stakeholders get access to up-to-the-minute dashboards. This gives everyone a transparent look at how the budget is performing, at any given moment.
- Improved Efficiency: When you automate cost tracking and resource allocation, your team spends less time on admin and more time on high-value, creative work.
Platforms like freispace are built specifically for the nuances of post-production. They link resource scheduling directly to financial tracking, so you instantly see the cost implications of your decisions as you make them.
The real power of a dedicated tool is turning financial data from a historical record into a predictive asset. It allows you to see where you're heading, not just where you've been, giving you the chance to course-correct before it's too late.
This real-time financial dashboard shows how integrated tools present complex data in an easy-to-understand visual format.
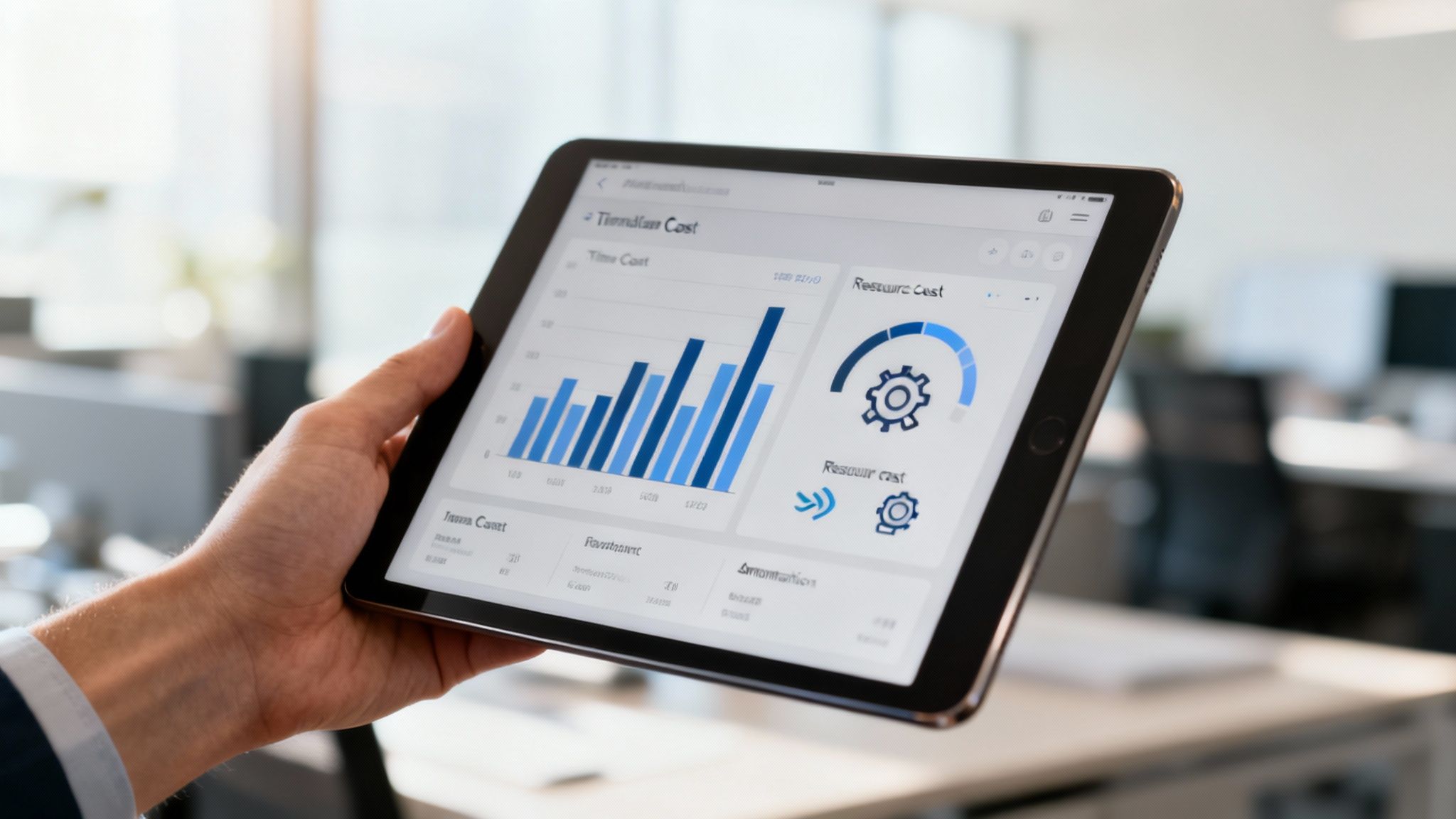

With a quick glance, a project manager can see budget vs. actuals, spot cost variances, and check resource utilisation. This makes for faster, much more informed decisions.
Scaling Financial Control for Large Investments
As projects balloon in scale and complexity, the need for a truly robust financial toolkit becomes non-negotiable. When you're managing large-scale investments, you need a system that can handle complicated financing structures and deliver detailed, reliable reporting.
Think about it on a massive scale. Successfully mobilising private finance for huge UK-backed climate programmes—which have raised an estimated £10.46 billion between 2011 and 2025—is completely dependent on structured project financing and painstaking monitoring. You can learn more about these financing patterns in a 2025 government report on UK International Climate Finance. This kind of large-scale capital management is simply impossible without sophisticated tools that can track different leverage mechanisms and provide standardised reporting across dozens of programmes.
Picking the right tool isn't just an operational upgrade; it's a strategic move. It fundamentally affects your ability to manage big investments with confidence, report on performance accurately, and ultimately, deliver your projects profitably and on schedule.
A Few Common Questions About Project Financial Management
Even the most buttoned-up financial plan is going to run into questions and challenges. That’s just the nature of the beast. Getting ahead of these common queries helps solidify the core ideas and gives you practical answers when you’re in a tight spot. Let’s dig into a few of the questions that come up time and time again.
What Are the Biggest Financial Challenges?
A few recurring gremlins can sneak in and completely derail a project's budget if you’re not watching closely. The most common culprit is scope creep, where those "small," unapproved changes start stacking up and quietly draining your funds. Another huge one is simply getting the numbers wrong from the start; inaccurate initial estimates create a wobbly foundation that’s almost impossible to build on successfully.
Poor resource management is another silent killer. If you misallocate your team or don't track their time properly, you'll see labour costs spiral and deadlines fly by. The fix? You have to be disciplined. That means a strict change control process, using bottom-up estimation for better accuracy, and having some form of real-time resource tracking in place.
The best defence against these challenges is a good offence: proactive monitoring and crystal-clear communication. Regular financial check-ins with your team and stakeholders kill surprises before they can grow and keep everyone grounded in the project’s financial reality.
How Does Financial Management Differ for Agile vs Waterfall?
Your project methodology has a massive impact on how you handle the money. The two big players, Waterfall and Agile, demand completely different financial mindsets.
- Waterfall Projects: This is the traditional, straight-line approach. The budget is usually fixed and signed off on right at the beginning, based on a super detailed scope. Financial control here is rigid—it's all about tracking every penny spent against that pre-approved baseline.
- Agile Projects: This method is all about iteration and embracing change. As you'd expect, financial management is far more fluid. Budgets are often handled in rolling waves, allocated per sprint or iteration. The focus isn’t on hitting a single, rigid number, but on delivering the most value you can within shorter, time-boxed financial cycles.
At the end of the day, Waterfall finance is about sticking to the plan. Agile finance is about adapting the plan to deliver value, even when things change.
What Is the Best First Step to Improve Project Finances?
If you feel like your project's finances are getting a bit messy, the best thing you can do is get brutally honest about where you stand right now. Start by creating a clear baseline. Pull up your current budget and compare it line-by-line with all your actual spending to date. This simple audit acts like a flashlight in a dark room—it will instantly show you where the money is really going and highlight any variances.
Once you have that clear picture, the next step is to make regular financial review meetings mandatory. Get them in the diary and treat them as non-negotiable. This single habit builds a rhythm of accountability and ensures financial performance is always part of the conversation, not a panicked afterthought.
Ready to swap out those clunky spreadsheets for automated, real-time financial tracking? freispace pulls your resource scheduling, budgeting, and reporting into one seamless platform. It gives you the clarity and control you need to bring projects in on time and on budget. Discover a smarter way to manage your post-production finances at https://freispace.com.